Observed COVID-19 Kidney Pathology and the Spike Protein
A new review by Muthya, et al., shows that Acute Tubular Necrosis and Collapsing Glomerulopathy are the most common kidney pathology findings.
The above graphs using data from the CDC (analysis by EthicalSkeptic) show the massive increase in renal failure since the introduction of the Spike Protein into the world. A review by Muthya, et al., published on Friday, shows how this increase can be directly tied to the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2.
The review discovered fourteen studies in the literature which consisted of 159 patients. The two most common kidney pathologies found were Acute Tubular Necrosis and Collapsing Glomerulopathy.
Fourteen studies consisting of 159 patients were included in this review. Acute tubular necrosis is the most common pathology followed by collapsing glomerulopathy, occurring in 40.1% and 28.9% of patients respectively.
It is well known that the Spike Protein interacts with ACE2, causing a loss of functionality. This loss of function directly negatively affects the kidneys. It is also well known that the Spike Protein induces the cytokine Il-6 (among others).
SARS-CoV-2 enters cells through the ACE2 receptor found in the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, vascular endothelium and kidneys.5 In the kidneys, ACE2 receptors are expressed in the brush border of the proximal tubular cells and, to a lesser extent, in podocytes.21 ACE2 has anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic effects by converting angiotensin 2 to angiotensin 1–7 and through the deactivation of bradykinin.5 SARS-CoV-2 infection of kidney cells downregulates ACE2 expression, promoting an inflammatory environment that contributes to AKI.5, 22 This is pertinent in CKD patients, particularly patients with diabetic kidney disease, who at baseline have downregulated ACE2 compared to control kidneys,21 potentially making them more susceptible to COVID-19-related kidney injury.22 The effects of the cytokine storm on the kidneys are uncertain. Cytokines interleukin-21 (IL-21), IL-8, tumour necrosis factor (TNF-a), IL-6 and IL-1β are raised following COVID-19 infection,5 and of these IL-6 has been identified as a dominant cytokine.23 IL-6 increases kidney vascular permeability and induces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines from kidney epithelial cells positively feeding back into the existing pro-inflammatory milieu.
Furthermore, and this is the most telling finding, the Spike Protein has been located in the kidney proximal tubules.
There is some evidence of direct infection of proximal tubule cells.22 In post mortem studies, immunohistochemistry has revealed SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid and spike antigens in the kidney proximal tubules,25, 26 and viral RNA has been found in proximal tubule cells.
What is the spectrum of kidney pathology associated with COVID-19?
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/imj.16540
If we look at what Acute Tubular Necrosis is, it becomes very clear how the Spike Protein is almost certainly responsible for this damage.
Coagulopathy, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), can also cause acute tubular necrosis.
Acute Renal Tubular Necrosis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507815/
Indeed.
Preexisting increased plasmin activity, recognized in hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, enhances the virulence and infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 by cleaving its spike protein [5]; thus, such activity is not only a determinant of the severity of COVID-19 but also may promote the development of DIC.
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in COVID-19 Setting: A Clinical Case Description
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10319425/
Given the massive increase in renal failure: The case can be clearly made that exposing the kidneys to the Spike Protein – in any form – would satisfactorily explain this massive increase.
Going back to the recently published review, one observation on the authors’ selection of literature to review truly caught my eye. In finding literature to review, they made a very deliberate search decision.
Databases were searched during June–July of 2022. The search terms were as follows:
Medline OVID: (covid 19 virus* OR ‘covid 19 infection’ OR sarscovid OR ‘severe acute respiratory syndrome*’ OR ‘wuhan coronavirus’ OR sars cov2 infection) AND (glomerulonephritis OR nephrotic syndrome* OR nephritic syndrome* OR nephrosis OR nephropathy OR renal tubular acidosis). NOT (vaccinat* OR vaccine) NOT (transplant*). Limit to all adults (18 plus years).
Scopus: (glomerulonephritis OR {nephrotic syndrome} OR {nephritic syndrome} OR nephrosis OR tubular necrosis OR nephropathy OR nephrosclerosis) AND (covid-19). AND NOT (transplant*) AND NOT (vaccinat* OR vaccine) AND NOT (pregnanc* OR pregnant OR haemodialysis OR dialysis OR hemodialysis) AND NOT (child* OR paediatric* OR pediatric* OR adolescent* OR neonat* OR newborn*). Limit to 2020–2022 AND subject area medicine AND limit language to ‘English’.
What is the spectrum of kidney pathology associated with COVID-19?
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/imj.16540
Hanging the elephant in the room with such a convenient trap door.



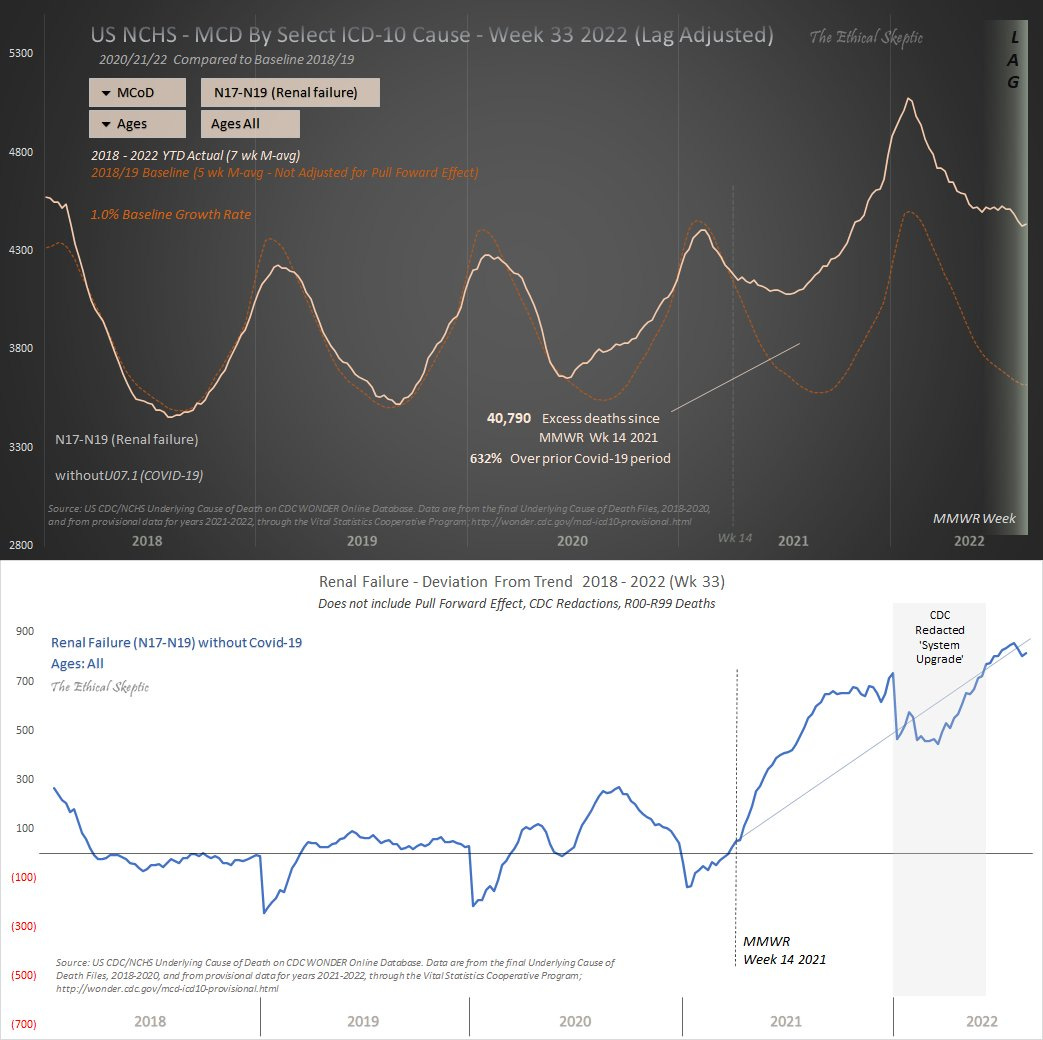
The two graphs at the beginning of this article are from EthicalSkeptic, not CDC. The data ES uses is from CDC, I think. But the graphs are ES' analysis.
I had a healthy unjabbed friend who suddenly presented with stage 4 kidney cancer and died less than one year later. He did have covid once after his diagnosis. Could it have been shedding from his jabbed wife? I struggle to understand as out of 8 in my bible study group, 6 of which were unjabbed, 2 were diagnosed with stage 4 cancers (kidney and colon). Both were previously healthy, unjabbed, and on no medications but both had jabbed wives.