My Most Important Finding to Date: The Spike Protein’s “Obliteration” of ACE2 and the Induction of Irreversible Oxidation via NOX5 Activation
Irreversible oxidation leads to systemic small vessel disease (fibrosis, etc.) explaining multiple organ damage post SARS-CoV-2/Spike Protein exposure.
Hypothesis of redox control of host cells in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Virus entry activates NOXs and inhibits Nrf-2 antioxidant response inducing ROS levels. NOX family members and their regulatory subunits are shown in detail on the left. NOX1-3 comprise two membrane subunits (NOX1-3 and p22phox), that represent the catalytic core of the enzyme, and different cytosolic subunits which translocate to membrane upon activation. NOX4 is constitutively active when associated with p22phox subunit. Nox5 and Duox1/2 activation involves Ca2+ binding to EF-hand domains. Hypothesis of redox control of host cells in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Virus entry activates NOXs and inhibits Nrf-2 antioxidant response inducing ROS levels. NOX family members and their regulatory subunits are shown in detail on the left. NOX1-3 comprise two membrane subunits (NOX1-3 and p22phox), that represent the catalytic core of the enzyme, and different cytosolic subunits which translocate to membrane upon activation. NOX4 is constitutively active when associated with p22phox subunit. Nox5 and Duox1/2 activation involves Ca2+ binding to EF-hand domains.
I have never given up my search for a fully satisfactory explanation for the multiple organ small vessel damage observed post SARS-CoV-2 infection and Spike Protein exposure. I have now discovered a mechanism that can fully explain how multiple organs are damaged. It starts with the Spike Protein’s universal “removal” of ACE2.
Here, we demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein activated intracellular signals to degrade ACE2 mRNA. The decrease of ACE2 and higher level of angiotensin (Ang) II were verified in COVID-19 patients. High dose of Ang II induced pulmonary artery endothelial cell death in vitro, which was also observed in the lung of COVID-19 patients. Our finding indicates that the downregulation of ACE2 potentially links COVID-19 to the imbalance of RAS.
Spike-mediated ACE2 down-regulation was involved in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9250808/
Why is this an absolutely devastating event? Because this loss of ACE2 activates the NOXs. In particular, it activates NOX5. ACE2 cleaves (cuts) ANG1. The product, Ang-(1-9), is then further metabolized into Ang-(1-7). However, you cannot get to Ang-(1-7) without first producing Ang-(1-9).
Why does this matter? Because Ang-(1-7) is critical for reducing the expression of NOX5, which induces irreversible oxidation in disease states.
Angiotensin-(1-7) prevents actin cytoskeleton derangement, monocyte adhesion, and migration impairment induced by thrombin via downregulation of ROS production. In addition, thrombin-induced Nox5 expression is involved in the production of ROS, and angiotensin-(1-7) decreases ROS through its inhibitory effect on Nox5 expression.
Angiotensin-(1-7) Inhibits Thrombin-Induced Endothelial Phenotypic Changes and Reactive Oxygen Species Production via NADPH Oxidase 5 Downregulation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5770656/
What are the end results of allowing NOX5 expression? Just about everything we are seeing in the body’s vasculature post SARS-CoV-2 infection/Spike Protein exposure. And it starts with the endothelium in the microvasculature. We know this is happening.
NOX2 were present in the cardiac microvascular endothelium. It has to be noticed that NOX2, NOX4 and NOX5 were also present in infiltrating inflammatory cells, most notably in neutrophils and macrophages. NOX4 was found in the endothelium of almost all intramyocardial blood vessels in all patients, without significant differences between controls and COVID-19 patients (data not shown). Immunofluorescent staining showed that NOX2 and NOX5 co-localized with the endothelial cell marker CD31, confirming the presence of these NOXes in the cardiac microvascular endothelium of patients with COVID-19.
NOX2 and NOX5 are increased in cardiac microvascular endothelium of deceased COVID-19 patients
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167527322016837
Clearly, studies need to be conducted for the effects on the microvasculature of other organs and systems. I believe the results will parallel the cardiac microvasculature findings.
Ultimately, the brief acute phase of COVID/Spike Protein exposure can start a deadly cascade. One that could take years to kill. The induction of NOX5 expression can begin the “closing off” of blood flow via microvascular destruction (fibrosis). I highly recommend viewing this entire lecture. It is superb.
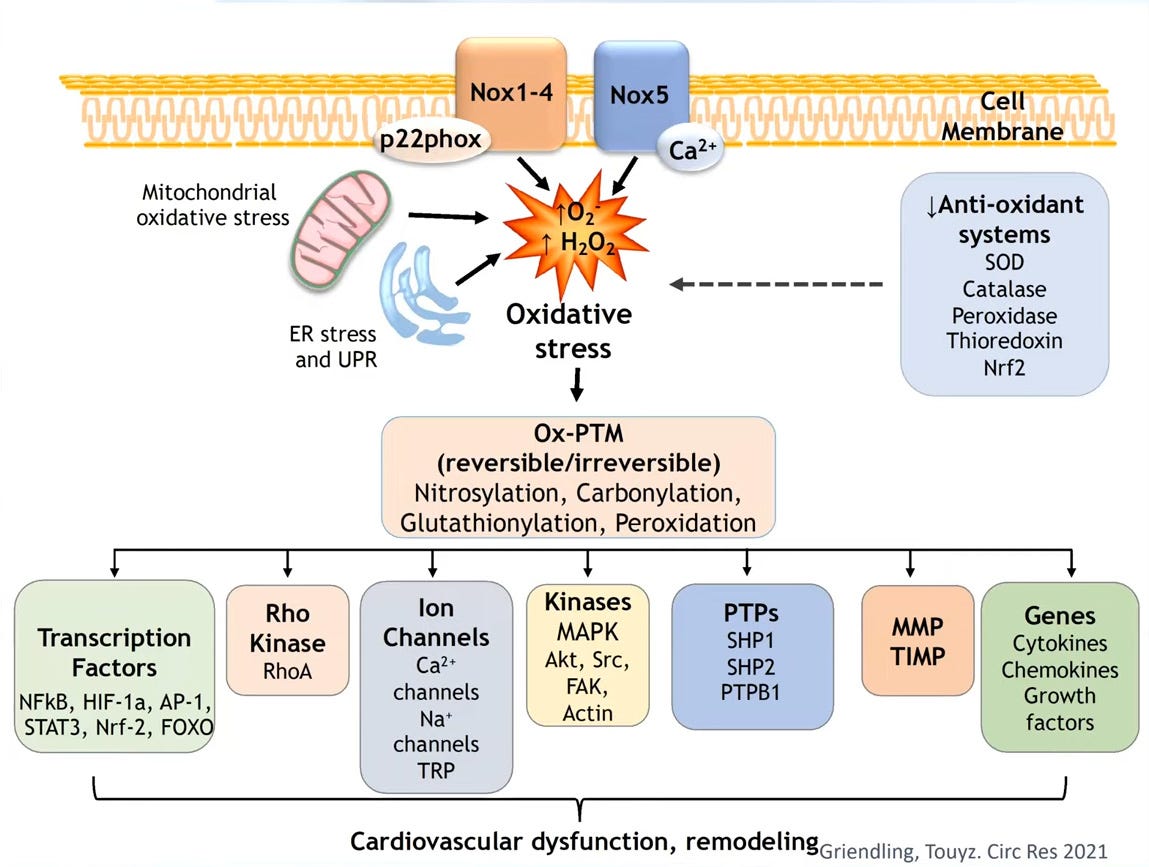
At the end of the day how does oxidative stress or an increase in the bioavailability of reactive oxygen species in cells actually have an impact on the downstream signaling molecules, some of which I've shared with you? We know the transcription factors, that ion channels, kinases, protein types in phosphatases genes are very very tightly regulated by the redox state of cells and we believe that this is due to the oxidative post-translational modification that these proteins undergo when you get an increase in oxidative stress. And I just want to highlight to you that post-translational oxidative modification is actually a very complex process but there are two components related to this there's a reversible oxidation and an irreversible oxidation and we believe that in pathological conditions where you start getting irreversible fibrosis irreversible cardiac vascular remodeling the cells and the signaling the molecules have undergone the irreversible oxidation it's sort of the last point of cell dysfunction.
The Vasculome in Hypertension and Small Vessel Disease - Grans Rounds with Rhian Touyz, PhD
It may be that intense anti-oxidative therapy during acture COVID/post Spike Protein exposure may help to prevent the induction of irreversible oxidation. I will be working on therapeutics.
Thank you, as always, for your support. I will continue to discover and solve.


Only social science doctorate here, so forgive ignorance, but I want to suggest some loose connections (no pun intended) I've observed in my condition & those of fellow sufferers. I've got severe hEDS + von willebrands--slow to clot, easy to bruise, easy to prolapse, easy to overextend joints, muscles rigid b/c compensating for overstretched elastic ligaments. I never got COVID. (Had J&J vax, w/ week of immediate discomfort, & menstruation 1 year after menopause.)
College of Charleston Ehlers Danlos research lab is finally identifying (preprint June 10) at least one common mutation (having to do w/ "kallokreins" ??) that contributes to defective connective tissue in hEDS . Hypermobility EDS leads to widespread systemic damage over lifespan, but has been medically "invisible" so that, combined w/ predominant female disability, has led to severe invalidation & misdx for decades.
I've noticed anecdotally that along w/ an inability to clot quickly, some of us have had unusually high "good cholesterol" & like many other ballerina looking female hEDS pts, didn't process carbs the way most people do (or see cholesterol changes) until menopause. Most of us have stayed very thin w/ a slight Marfanoid yet curvey phenotype (scoliotic lumbar spine extending outward, highly defined ankles vis a vis calves). We're able to avoid "metabolic" issues like most Americans consuming juices, grains, potatoes per misguided Food Pyramid. It's like even w/o ketogenic diet (which I swear by now), our livers were pre-emptively protected from early diabetes, until menopause.
I just wonder about insights re COVID, heart issues, & metabolism, that might be gained from considering phenotypes who seem to have some protection from these issues as a tradeoff with other often disabling conditions. By comparing these conditions, you might also generate useful hypotheses about connective tissue disorders and/or role of Kallikreins.
I know I'm throwing out a lot here but wanted to bring to your attention the research interests of the C. of Charleston lab (& those at Johns Hopkins/U Baltimore) on connective tissue disorders & areas of potential mutual benefit. Thx for your indefatigable work on the genetically engineered harms of this virus.
I plan to keep chewing nicotine gum…I saw the connection with the ACE2 in 2020, and never got the Vid. Great research you continue to provide us with to read Walter. You are appreciated!