IS DEFIBROTIDE AN IMPORTANT TREATMENT FOR SPED, COVID AND LONG COVID?
Early treatment may provide endothelial protection and it may treat Long COVID.
I have promised to look for solutions. I believe I have found an important one.
Interestingly, SPED has all the hallmarks of the endothelial damage of SEPSIS.
After exposure to patients' sera, there was a progressive endothelial cell activation in correlation with sepsis severity, with a proinflammatory and prothrombotic phenotype, exhibiting significantly increased expression of adhesion receptors at the surface (intercellular adhesion molecule-1, p < .05 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, p < .05); higher production and release to the extracellular matrix (ECM) of von Willebrand factor (p < .001); augmented thrombogenicity of the ECM toward platelets (p < .001); and increased phosphorylation of intracellular p38MAPK.
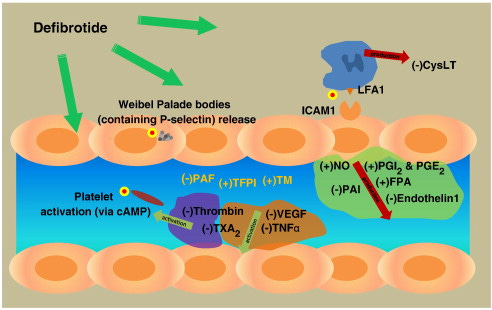
A drug called Defibrotide was able to prevent all of the above changes.
Defirbotide (DF) prevented these changes in all groups. Markers of endothelial damage increased progressively in association with the severity of septic syndromes. The endothelium is therefore an important therapeutic target to prevent complications of sepsis. DF shows promising potential to modulate the endothelial damage associated with sepsis and may constitute a pharmacological tool to decrease its sequelae including multiorgan failure.
Progressive endothelial cell damage in correlation with sepsis severity. Defibrotide as a contender
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33872468/
An editorial from August sees precisely what I see in the therapeutic. I believe it is CRITICAL to trial this as early treatment, in those hospitalized and in those suffering from Long COVID. I believe this drug will prove to be extremely beneficial.
Defibrotide works via multiple mechanisms of action, specifically targeting several pathways involved in the pathogenesis of thrombotic phenomena in COVID-19, as discussed by Frame et al11 in their article. Indeed, other authors have indicated that defibrotide, besides its profibrinolytic activity, can exert antithrombotic effects through other mechanisms involving antiinflammatory and antioxidant pathways.4 Defibrotide hinders the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, by activated macrophages and mononuclear cells; inhibits ROS generation by activated monocytes/macrophages; and can restore nitric oxide generation under conditions of oxidative stress. Furthermore, in vitro and ex vivo work showed that defibrotide inhibits the TF expression stimulated by inflammatory molecules, raises the synthesis of thrombomodulin in endothelial cells, downregulates prothrombinase action, decreases thrombin-mediated platelet aggregation, and increases platelet- and leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions. Defibrotide is also able to reduce the activity of heparanase, which is a key mediator of macrophage activation and polarization.
Defibrotide Has a Role in COVID-19 Therapy
https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(22)00887-X/fulltext
The drug has been studied in COVID with promising results.
Conclusion: Treatment with DF in pts with grade 5 WHO COVID 19 ARDS does not induce bleeding, and is associated with rapid restoration of respiratory function (73% of pts). Notably, no oxygen support was needed at discharge and a 1-month OS rate of 89% was observed, which is higher than historical controls (77%) treated in the same setting.
Use of Defibrotide in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia; Results of the Defi-VID19 Phase 2 Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8701766/
I believe Defibrotide, in concert with the natural endothelium-protective substances Jennifer Depew and I have discussed in our substacks, may substantially improve the lives and prognosis of those suffering from this novel pathogen.



Dear Walter ❤ thank you for the most beautiful news this morning!
You made me so haaaaaaapyyyyyy! You are brilliant, trustworthy and a great humanitarian 🤗❤💜💓💗💜💕💖💞.
Consider yourself & your cat hugged forever 🤗❤💓💕💗💙💓💚💛❤💘💙💗🧡💙💜💟
What about non prescription options? Seems that Nattokinase, Lumbrokinase and Serrapeptase continue to be on the top of the list, especially Natto: https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/27/17/5405/htm
Walter, I am curious on your thoughts on if TUDCA could be helpful as well, given it has amyloid degrading properties and is currently being studied on various neurodegenerative diseases. Given there seem to be prion like diseases going on in some, it seems liek a potentially helpful supplement to use, and is easily found over the counter.
"In recent years, hydrophilic bile acids, particularly tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), have shown important anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective activities, with numerous experimental and clinical evidence suggesting their possible therapeutic use as disease-modifiers in neurodegenerative diseases. Experimental evidence on the mechanisms underlying TUDCA’s neuroprotective action derives from animal models of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and cerebral ischemia. Preclinical studies indicate that TUDCA exerts its effects not only by regulating and inhibiting the apoptotic cascade, but also by reducing oxidative stress, protecting the mitochondria, producing an anti-neuroinflammatory action, and acting as a chemical chaperone to maintain the stability and correct folding of proteins"
Full study here cited above: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9166453/
As well: Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Enhances Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Neural Stem Cell Pool, and Early Neurogenesis in Adult Rats https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317096977_Tauroursodeoxycholic_Acid_Enhances_Mitochondrial_Biogenesis_Neural_Stem_Cell_Pool_and_Early_Neurogenesis_in_Adult_Rats