Friday Hope: Vitamin D Encore: Reduction of Cell Adhesion Molecules
Yet another mechanism of Vitamin D gives us additional understanding of this powerful COVID therapeutic.
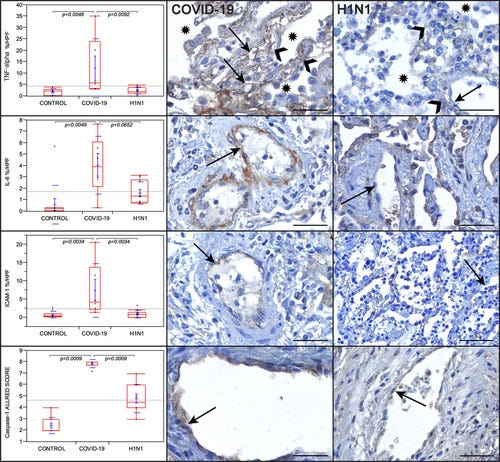
Graphs showing the comparison between the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), H1N1, and control groups regarding TNF (tumor necrosis factor)-α, IL (interleukin)-6, ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1); in percentage per high-power fields (HPF), and caspase-1 tissue expression (in Allred score). TNF-α is remarkably high in the alveolar septal cells (black arrowheads) and the alveolar-capillary cells (black arrows) of the COVID-19 case than in the H1N1 case. Alveolar lumens are identified with asterisks. IL-6 tissue expression is remarkably high in the endothelial cells (black arrows) of the COVID-19 case than in the H1N1 case. ICAM-1 tissue expression is remarkably higher in the endothelial cells (black arrows) of the COVID-19 case than in the H1N1 case. Caspase-1 is higher in the endothelial cells of the COVID-19 case than in the H1N1 case. Kruskal-Wallis test was used for P values. Scale bars=50 µm.
If you have been following the course of my research, you will know that evidence is mounting demonstrating that, ultimately, COVID-19 and its Spike Protein are inducing a disease of Cell Adhesion Dysregulation. I refer you to my previous post and the above graphic for insight.
Throughout the course of the pandemic, it has been observed that those with high Vitamin D levels have fared exceptionally well when infected with SARS-CoV-2. There have been many obvious reasons for this, and there have been some interesting surprises along the way. I have discovered yet another way that makes this wonder molecule extremely effective against SARS-CoV-2.
After researching natural ways to reduce levels of Cell Adhesion Molecules, I was both surprised – and not – to discover that Vitamin D does exactly this. It was akin to wondering who sent you an anonymous message only to chuckle when you discovered it was an old friend.
The endothelial cell adhesion expression is directly responsible for the endothelial dysfunction. The Spike Protein causes the endothelium to DAMAGE ITSELF.
The endothelial expression of ICAM-1 was significantly higher in the COVID-19 group than H1N1 and control groups. The activated endothelial cells can express the ICAM-1 molecules that could attract leukocytes (endotheliitis) and transmit intracellular signals leading the sustained proinflammatory status. The proinflammatory condition would result in a systemic endothelial dysfunction and lead to the loss of its integrity via endothelial cell death.5 The persistent inflammatory signaling of these adhesion molecules would also contribute to later thrombotic events.
Endothelial Dysfunction and Thrombosis in Patients With COVID-19—Brief Report
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314860
Cellular senescence was associated with an increased level of the endothelial adhesion molecules vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), which have in vitro leukocyte attachment potential. Inhibition of senescence or SASP function prevented VCAM-1/ICAM-1 expression and leukocyte attachment. Taken together, we identified that human endothelial cells exposed to cell culture supernatant derived from SARS-CoV-2 spike protein expression displayed cellular senescence markers, leading to enhanced leukocyte adhesion.
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Paracrine Senescence and Leukocyte Adhesion in Endothelial Cells
https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/JVI.00794-21
And this is where, once again, Vitamin D comes to our aid.
The guiding question was: “In diseases whose complications lead to vascular dysfunction and thrombus formation, is vitamin D supplementation associated with CAM concentrations?”. Studies investigating CAM in all age groups of both sexes using any type and dose of vitamin D supplements were included. Of 617 initially obtained articles, 9 met the inclusion criteria. The articles were divided based on clinical outcomes: Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), Type II Diabetes Mellitus (DM-II), Metabolic Syndrome (MS) and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Four articles reported reduced serum CAM concentrations (two with CKD, one with MS and another with DM-II).
Vitamin D and its effects on cell adhesion molecules: A systematic review
https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-2378202/v1/b59c559d-2dcd-423d-ad1f-58d7592d209c.pdf?c=1679283868
Please note how the diseases/conditions studied happen to be significant comorbidities for severe COVID.
The evidence is currently limited – but convincing. I will continue to investigate the inhibition of Cell Adhesion Molecules as this may be the most important way to treat/prevent COVID, Long COVID and Spike Protein-related pathologies.
As always, thank you for your support. Blessings for a peaceful weekend.



Thanks for this Walter. Are you aware of the research of MIT Phd Seneff who discusses how Vit D supplementation can give our bodies a false signal, so we don't produce enough of the right kind of D through sulfation by UV-B light and cholesterol?:
https://romanshapoval.substack.com/p/why-vitamin-d-supplements-dont-work
Why UV-B from the Sun is our ultimate supplement:
https://romanshapoval.substack.com/p/vitamindpodcast#details
Thank you Walter. Excellent news. Have a great weekend. Peace.