Systemic Inflammation: The Raison d’Être of the Spike Protein
Like so many malevolent flowers, the Spike Protein “blooms” inflammation in organs, leading to injury and death.
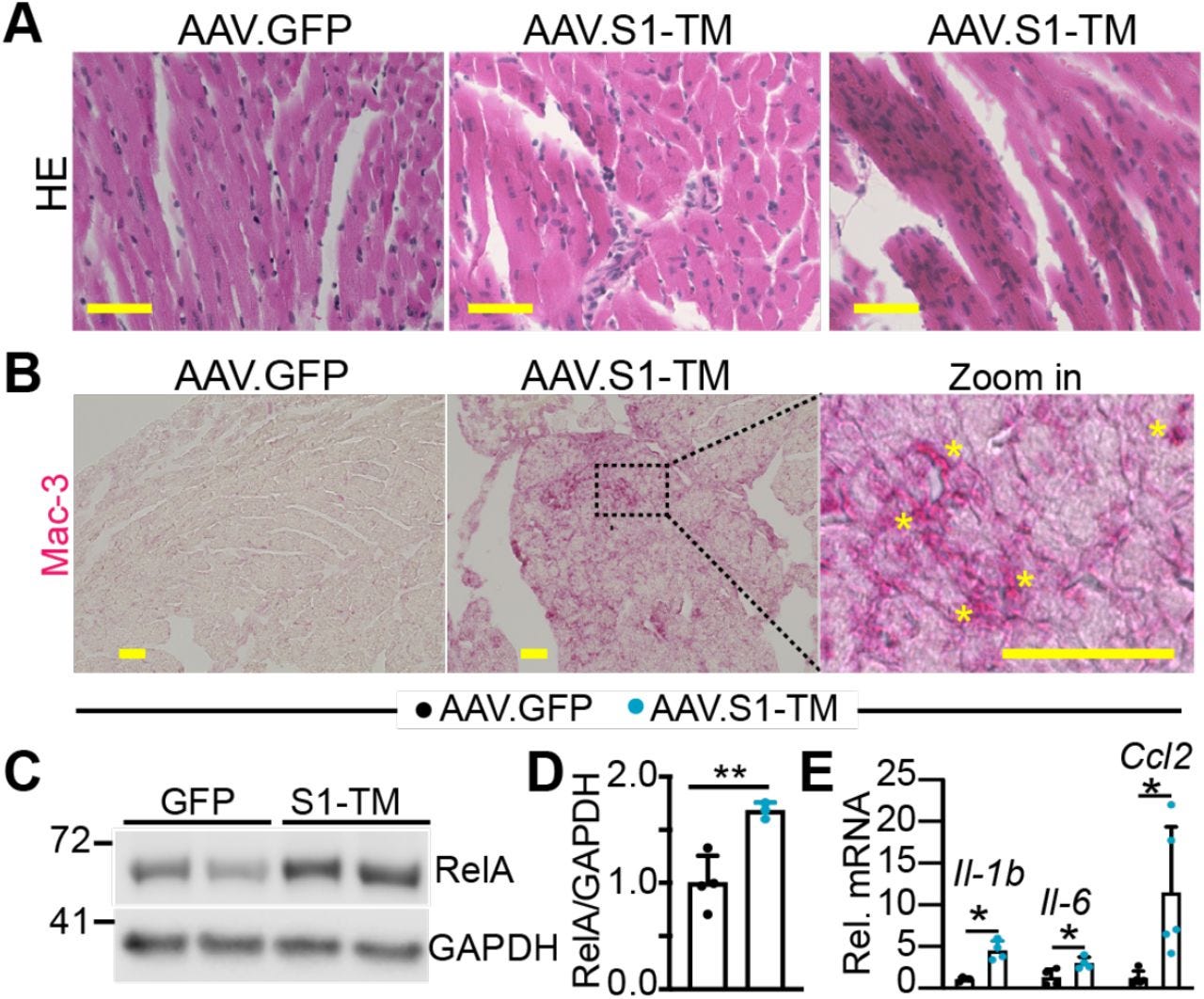
S1-TM induces cardiac inflammation.
A. HE stained myocardium. Scale bar = 50μm. B. Immunohistochemistry staining of Mac-3 in myocardium. Alkaline phosphatase based detection system was used to visualize Mac-3 positive cells. In the zoom-in image, yellow stars indicate macrophage clusters. Scale bar = 50μm. C. Immuno Blot of RelA. D. Densitometry quantification of RelA. RelA protein levels were normalized to GAPDH. N=3-4. E. qRT-PCR measurement of Il-1b, Il-6 and Ccl2. N=4-5. D,E, Student’s t test, *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.
Selectively expressing SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein S1 subunit in cardiomyocytes induces cardiac hypertrophy in mice
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.06.20.448993v1.full
Please study the above image carefully.
Now please study this one.
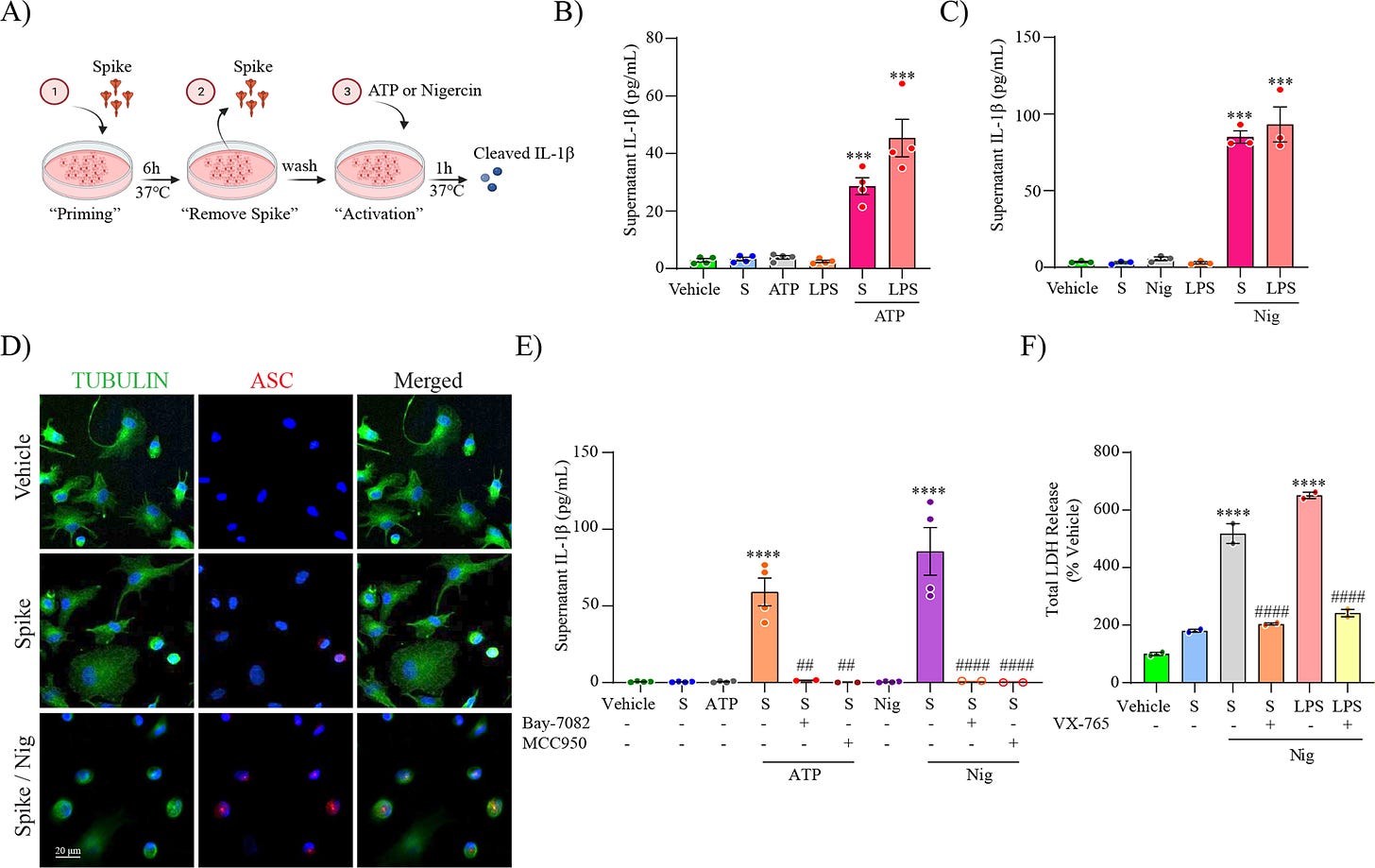
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein primes the NLRP3 inflammasome through NF-kB.
Schematic representation for spike priming experiments (6 h) followed ATP or Nigericin (Nig) activation (1 h) (A). Level of secreted IL-1β in unprimed or S-clamp-primed MDMi (S; 50 μg 6 h) followed activation with ATP (5 mM, 1 h) in (B) or Nigericin (Nig; 10 μM, 1 h) in (C). In both LPS-primed cells were used as a positive control (200 ng/ml 3 h). Immunofluorescence staining of vehicle or S-clamp (S; 50 μg 6 h)–primed MDMi, activated with Nigericin (Nig; 10 μM, 1 h) showing tubulin (green) and the formation of a characteristic inflammasome ASC speck (red) are shown in (D). Scale bar 20 μm. ATP and Nigericin–mediated IL-1β secretion (supernatant) in vehicle (untreated) or S-clamp-primed MDMIs exposed to ATP (5 mM, 1 h) or Nigericin (Nig; 10 μM, 1 h) in presence or absence of Bay 11-7082 (3 μM) or MCC950 (10 μM) are shown in (E). Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay for quantification of caspase-1–dependent pyroptosis in S-clamp (S; 50 μg 6 h) primed cells activated with Nigericin (Nig; 10 μM, 1 h) in (F). LPS-Nigericin and VX-765 (20 μM) were used as positive controls. Data are means ± SEM from at least 3 independent donors. ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001 by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test.
SARS-CoV-2 drives NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human microglia through spike protein
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-022-01831-0
Next.
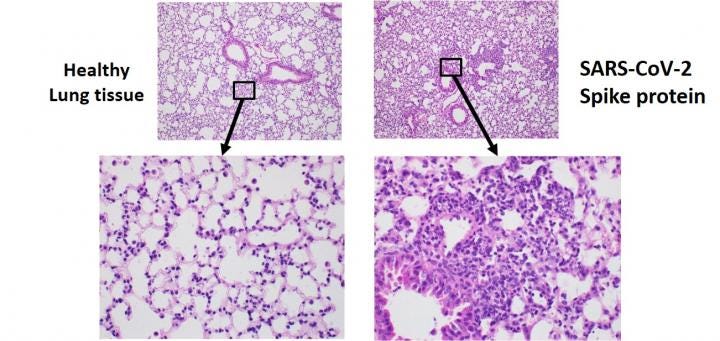
Using a newly developed mouse model, researchers found that exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alone was enough to induce COVID-19-like symptoms including severe inflammation in the lungs. The left images show healthy mouse lung tissue while the right images show tissue from mouse lungs exposed to the spike protein.
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alone may cause lung damage
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/490426
And.
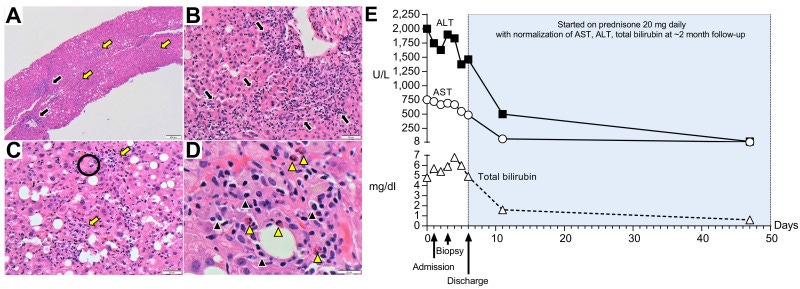
(A) Low-magnification (40x) shows pan-lobular hepatitis (black arrows: portal inflammation and yellow arrows: lobular inflammation). (B) Medium-magnification images (200x) show a portal tract with an intense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate effacing the interface with rosette formation and (C) lobular activity with scattered hepatocyte necrosis (Black circle: acidophilic bodies). (D) At high magnification (600x), the inflammation consists primarily of lymphocytes with plasma cells (black arrowheads) and eosinophils (yellow arrowheads). (E) Trends of plasma ALT, AST and total bilirubin over time.
Autoimmune hepatitis developing after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine: Causality or casualty?
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)00237-3/fulltext
Continuing.
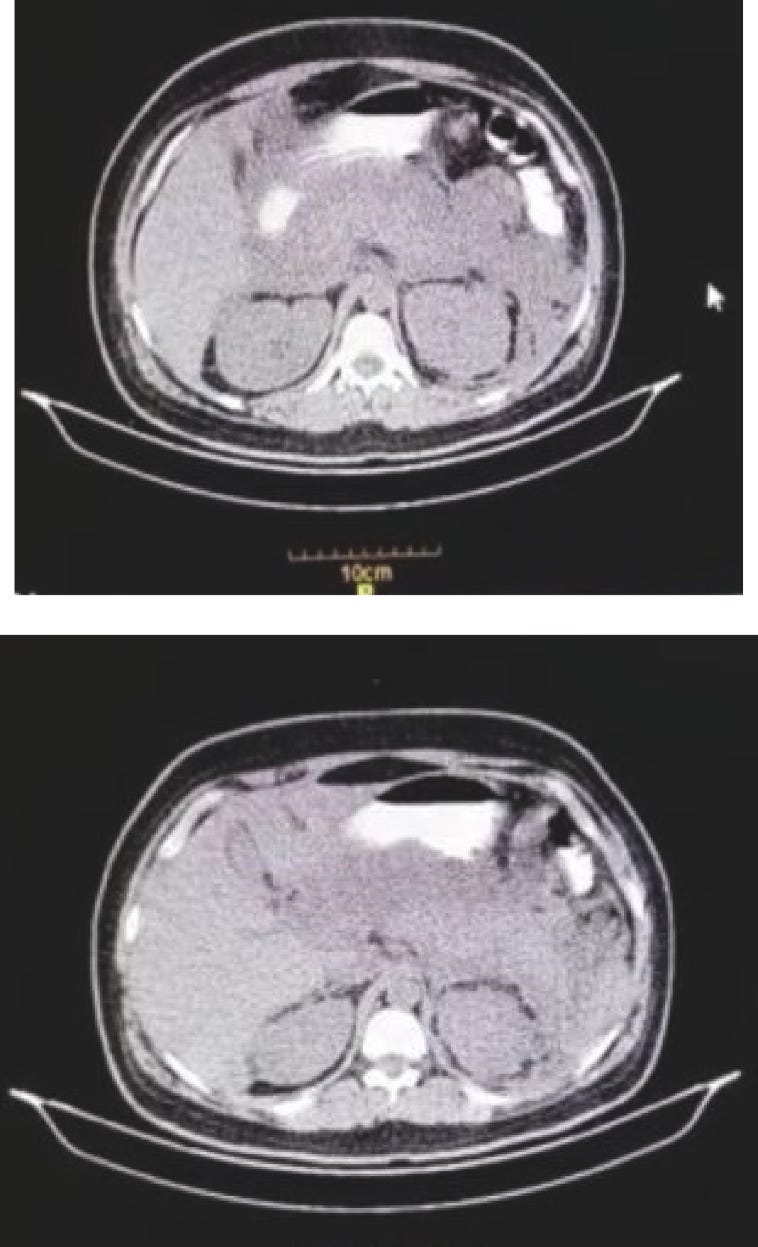
Computed Tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen. Homogeneous enlargement of the pancreas, extensive peri-pancreatic fat and peri-pancreatic fluid was observed.
Acute pancreatitis following COVID-19 vaccine: A case report and brief literature review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9840226/
But, of course.
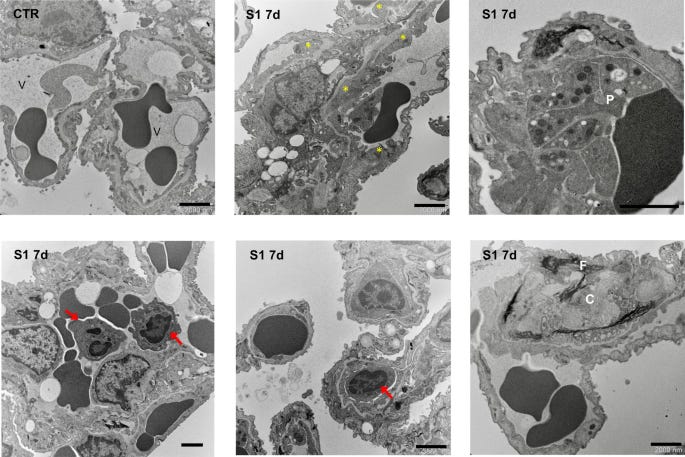
S1 injection induces endothelial ultrastructural changes in lung tissue of hACE2-KI mice. Ultrastructural analysis of lung alveolar tissue from CTR and S1-injected mice at 7d. In CTR mice, thin vascular endothelial cells form the inner lining of alveolar capillary (V). Mice injected with S1 at 7d show areas of thickening of endothelial cells (yellow asterisks), associated with activated platelets (P), inflammatory cell accumulation (red arrows), including neutrophils and monocytes, and material with fibrillar aspect (F) and collagen (C) deposition. Scale bars: 2000 nm.
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces lung endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombo-inflammation depending on the C3a/C3a receptor signalling
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-38382-5
I could go on, but I am certain you see no need to.
Now. Let’s read a few paragraphs together, shall we?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurologic disease that is characterized by patchy inflammation, gliosis, and demyelination within the central nervous system (CNS). It is the third most common cause of disability in adults between 18 and 50 years of age.
Chronic Pain in Multiple Sclerosis: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Impact on Quality of Life in an Australian Community Cohort
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1526590007006396
IBD encompasses a group of chronic, idiopathic, and recurring inflammatory disorders affecting the GI tract. The two primary forms of IBD are Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC)40–42. The clinical manifestations of IBD vary depending on the location and severity of inflammation within the GI tract. CD is characterized by patchy inflammation that can affect the full thickness of the bowel wall throughout the small and large intestines42–45. There may be areas of healthy tissue between inflamed sections (skip lesions).
Unraveling the Link between Periodontitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Challenges and Outlook
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10462160/
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is patchy inflammation, fibrosis, and strictures of the bile ducts that has no known cause.
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/hepatic-and-biliary-disorders/gallbladder-and-bile-duct-disorders/primary-sclerosing-cholangitis-psc
Pancreatic fibrosis and atrophy were graded according to the scoring system of Klöppel and Maillet [21]. Perilobular fibrosis was defined as the presence of connective tissue in the interlobular spaces [21]. Intralobular fibrosis was defined as the presence of connective tissue extending from the perilobular fibrosis to the acinar lobules with fibrous replacement of the acinar cells [21]. Fibrosis was graded as an extension of the fibrosis into the acinar lobules with partial (mild: 10–40%; moderate: 40–80%) or (almost) complete (severe: 80–100%) fibrous replacement of the acinar cells. Acinar atrophy was defined as the destruction of the acinar cells and fibrosis replacement. Acinar atrophy from the tumor specimen slides was similarly graded as follows: partial (mild: 10–40%; moderate: 40–80%) or (almost) complete (severe: 80–100%) fibrous replacement of the acinar cells. Chronic inflammation was graded as mild, moderate and severe according to the number of mononuclear inflammatory cells (see Additional Figs. 1 and 2). Mild and moderate chronic inflammation were characterized by patchy inflammation. Moreover, moderate chronic inflammation exhibited higher numbers of mononuclear inflammatory cells than mild chronic inflammation. A diffuse pattern of inflammation was evident in severe chronic inflammation. Duct changes included the distortion of ducts, periductal fibrosis, the presence of protein plugs, calculi, epithelial destruction, periductal inflammation and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) [21].
Pancreatic fibrosis, acinar atrophy and chronic inflammation in surgical specimens associated with survival in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8721973/
And these are just the tip of the iceberg. All of the above are associated with post COVID/Spike Protein exposure.
Like a malignant protagonist who invades the Parable of the Seed Sower, SARS-CoV-2 (or mRNA) casts its Spike Protein far and wide. In some (many) places it takes root and then, as mentioned above, proceeds to “bloom” in patches of inflammation. Damaging and destroying organs and tissue.
Perhaps the most alarming manifestation is that of the incidents of Myocarditis.
Autopsies revealed patchy inflammation suggesting that sudden arrhythmic death could have occurred due to a re-entrant ventricular arrhythmia culminating in sudden cardiac death. The authors in these cases concluded that the cause of death was COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis.
Autopsy findings in cases of fatal COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ehf2.14680
Obviously, the heart can exhibit the most dramatic and immediate effects. But my point is that there are other organs, other systems that are being equally affected by the inflammation of the Spike Protein. It’s like the classic horror movie The Blob. Areas of inflammation arise, develop, very likely merge.
Yet, there is hope. We can stop the Spike from binding. We can reduce levels of inflammation. We can degrade its microclots. We can protect our Endothelium as well as other organs. The Spike is a supreme opportunist. Don’t give it a chance.



Pomegranate peel prevents inflammasone creation. It inhibits NFkB.
Thank you Walter. May God bless you and continue to guide you. Peace.