Friday Hope: Taurine: Halting the Cytokine Storm and Treating Long COVID
Taurine also shows great promise in reducing the risk of Metabolic Syndrome and slows aging in mice and primates.
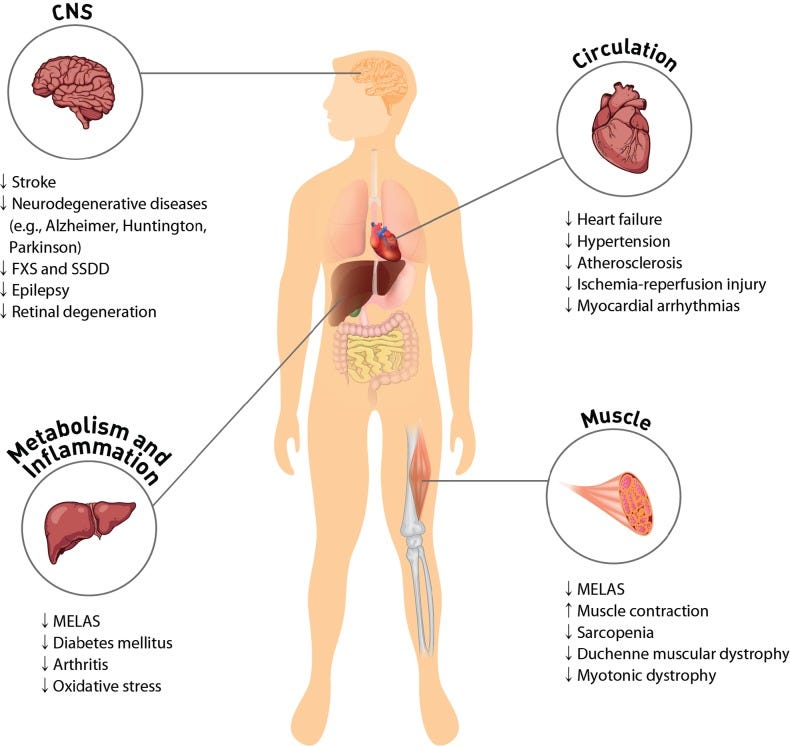
Taurine-mediated protection against pathology and disease. High concentrations of taurine in most cells regulate physiological function of excitable tissues and mitochondria. Taurine protects CNS by decreasing ER stress and antagonizing neurotransmitter receptors of GABAA, glycine and NMDA. Protection of the cardiovascular system by taurine occurs through regulation of cell signaling, such as Ca2+ transport, ROS generation and protein phosphorylation. Supplementation of taurine ameliorates symptoms of MELAS and diabetes mellitus. The anti-inflammatory activity of taurine involves either the formation of taurochloramine in neutrophils or the attenuation of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 in inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Taurine depletion or taurine transporter KO leads to cardiac and skeletal muscle dysfunction. Taurine prevents sarcopenia in aged person by minimizing gradual muscle loss. CNS: central nervous system; FXS: fragile X syndrome; SSDD: succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency; MELAS: mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes.
This week I have exciting news to report. Instead of an herb, today we will discuss an amino acid: Taurine. Over the past year much has been discovered about this amino acid. It has the ability to halt the cytokine storm of COVID as well as the ability to potentially treat Long COVID. Additionally, Taurine appears to slow aging in mice and primates while reducing the risk of Metabolic Syndrome.
Please read this article carefully and please, as always and especially here, consult your primary care provider before supplementing Taurine. It must be used with care and caution and may not be for everybody. This is a work of medical research and not medical advice.
What is Taurine?
Taurine (/ˈtɔːriːn/), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a non-proteinogenic naturally occurred amino sulfonic acid that is widely distributed in animal tissues.[1] It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight.
Taurine is named after Latin taurus (cognate to Ancient Greek ταῦρος, taûros) meaning bull or ox, as it was first isolated from ox bile in 1827 by German scientists Friedrich Tiedemann and Leopold Gmelin.[2] It was discovered in human bile in 1846 by Edmund Ronalds.[3]
Although taurine is abundant in human organs with diverse putative roles, it is not an essential human dietary nutrient and is not included among nutrients with a recommended intake level.[4] Taurine is commonly sold as a dietary supplement, but there is no good clinical evidence that taurine supplements provide any benefit to human health.[5] Taurine is used as a food additive for cats (who require it as an essential nutrient), dogs, and poultry.[6]
Taurine concentrations in land plants are low or undetectable, but up to 1000 nmol/g wet weight have been found in algae.[7][8]
Taurine
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taurine
As a side note, isn’t it INTERESTING how virtually every supplement entry in Wikipedia invariably makes the rubbish claim that “there is no good clinical evidence that XXXXX supplements provide any benefit to human health?” Good news in there, however, for our feline readers (I’m looking at you, Ferdinand!)...
So, it has been known for quite some time that Taurine possesses good anti-inflammatory properties.
The content of taurine in the neutrophil is high, representing about 50% of the total free amino acid pool. The two primary functions of taurine in the neutrophil are anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions. ROS are produced by the neutrophil as a weapon to kill pathogens, with one of those ROS being hypochlorous acid (HOCl). Myeloperoxidase-catalyzes the formation of taurine chloramine (TauCl) from taurine and HOCl. Because TauCl is a less potent oxidant than HOCl, the neutralization of HOCl represents one of the important antioxidant mechanisms of taurine. The myelperoxidase-catalyzed reaction is also responsible for the anti-inflammatory activity of taurine, as TauCl inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines (Marcinkiewicz et al., 1995; Park et al., 1997; Barua et al., 2001), attenuates elevations in nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 (Park et al., 2000; Chorazy-Massalska et al., 2004; Kim et al., 2007), decreases the activity of matrix metalloproteinases and initiates leukocyte apoptosis to terminate acute inflammation (Klamt and Shacter, 2005). For a detailed discussion of the anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic actions of taurine please refer to the extensive review by Marcinkiewicz and Kontny (2014).
Effects and Mechanisms of Taurine as a Therapeutic Agent
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5933890/
Therefore it makes total sense that Taurine would be looked at as a treatment for acute COVID, where, indeed, it may be very beneficial by halting the cytokine storm.
If adequate therapy is not given at the proper moment, the COVID-19 disease can be lethal. According to research findings, “approximately 20% of COVID-19 patients tend to have a severe or critical disease, with a mortality rate of 50% or more in critical cases” [133–135]. The polarization (change from the M2 to the M1) of alveolar macrophages caused by SARS-CoV-2 could disrupt efferocytosis, preventing neutrophil death and perpetuating the inflammatory process [121, 136]. It has been postulated that much of the damage to lung cells in complicated COVID-19 cases is associated with an increase in HOCl generation by neutrophils and M1 macrophages rather than by the virus itself [73]. Taurine is a powerful scavenger for HOCl, and so neutralizes its harmful effects, according to compelling data [100]. Taurine also restricts the generation of all pro-inflammatory molecules linked to the cytokine storm, prevents damage to the lungs by decreasing oxidative stress, and promotes the resolution of the inflammatory process [98–101]. Neutrophil LF degranulation driven by taurine may have direct antiviral actions against SARS-CoV-2, suppressing viral replication [126].
Early taurine administration as a means for halting the cytokine storm progression in COVID-19 patients
https://www.explorationpub.com/uploads/Article/A100188/100188.pdf
More recently, it has been discovered that Taurine may be a key factor in identifying and potentially treating those suffering from Long COVID.
Other molecules in the panel involved in energy metabolism include 2-aminoadipic acid (an established predictor of diabetes), taurine, and acylcarnitines.59,60,61,62 Spermidine is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effects and ability to promote nitric oxide production to improve mitochondrial function and biogenesis, whereas asymmetric dimethylarginine elicits opposite effects.63,64 Suppression of the taurine pathway during convalescence was associated with worse health-related quality-of-life and adverse outcomes. Interestingly, taurine has been shown to alleviate oxidative stress and promote beneficial metabolic effects while protecting the cardiovascular system.65,66 Across various animal models, taurine administration improved strength, depressive behavior, memory, and other hallmarks of aging through attenuating cellular senescence, mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA damage, and chronic inflammation.67 However, the longitudinal safety and efficacy of taurine supplementation to alleviate PASC symptoms in humans remains to be determined. Collectively, these data indicate that persistently altered cellular bioenergetics and mitochondrial dysfunction constitute a significant risk factor for developing PASC that could be targeted to improve clinical outcomes.
And
Fourthly, taurine supplementation can potentially alleviate long COVID burden based on the strong and consistent correlation between taurine levels with PASC symptoms and quality of life. Lastly, the observed dysregulation in microbiota-derived metabolites such as TMAO and phenylacetylglutamine concomitant with findings of gut dysbiosis in long COVID represents an attractive therapeutic target.32
Sequential multi-omics analysis identifies clinical phenotypes and predictive biomarkers for long COVID
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(23)00431-7
Beyond therapeutic potentials for COVID and Long COVID, recent evidence shows that Taurine may also prevent Metabolic Disease and may have the capacity to slow aging.
In conclusion, our meta-analysis of RCTs highlights taurine supplementation’s significant potential in mitigating key MetS risk factors, including reductions in SBP, DBP, FBG, and TG levels. This underscores its potential as a complementary therapeutic agent for MetS management, offering a multifaceted approach to glycemic control and cardiovascular health. Future clinical trials should focus on determining optimal taurine dosage and treatment duration, especially in MetS-susceptible populations.
Taurine reduces the risk for metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41387-024-00289-z
Aging is associated with changes in circulating levels of various molecules, some of which remain undefined. We find that concentrations of circulating taurine decline with aging in mice, monkeys, and humans. A reversal of this decline through taurine supplementation increased the healthy lifespan in worms and mice, and healthspan in monkeys. Mechanistically, taurine reduced cellular senescence, protected against telomerase deficiency, suppressed mitochondrial dysfunction, decreased DNA damage, and attenuated inflammaging. In humans, lower taurine concentrations correlated with several age-related diseases, and increased after acute endurance exercise. Thus, taurine deficiency may be a driver of aging as its reversal increases healthspan in worms, rodents and primates and lifespan in worms and rodents. Clinical trials in humans seem warranted to test whether taurine deficiency might drive aging in humans.
Taurine deficiency as a driver of aging
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abn9257
I am quite impressed by this humble amino acid. So much knowledge, therapy, nutrition and guidance are available to all of us who seek it out. As it was determined thousands of years ago: Seek and ye shall find.
It is another glorious Spring Friday here in Vermont. Crystal clear skies and a perfect temperature of 70 degrees. I wish all a fantastic Memorial Day weekend for those in the States, and a fantastic weekend in general for everyone. Thank you, as always, for your readership, support and dialog. I am particularly overwhelmed by the following of this Substack, which has increased by 200 this week alone. I will always keep my promise to never put my research behind a paywall. I do ask, that as only 2.3% (326 of 14,100) of readers are Paid Subscribers, if you are comfortably able to, to please consider becoming a Paid Subscriber or donating via PayPal at https://wmcresearch.org/donate/.



What amazes me is how many outpatient supplements or meds are available to slow or stop the cytokine storm, but none was endorsed by mainstream practitioners or facilities. Bad, bad, bad.
I am an lc patient..early on I read about taurine as a "brain calmer" it's effects on reducing the feeling of anxiety from long covid. I started taking it & immediate results. Cardiovascular, CNS, aging and more... taurine is part of my daily regimen. I love reading about your findings to try more things...or to give additional credibility to the actions I already take. Have a great 3 day weekend