Burned Alive: The Skin, The Endothelium, The Spike Protein and Spike Protein Disease/Acute/Long COVID
If we look at the endothelium as the skin, all can be explained by surface area “burns” (injury).
This is a very important post.
Building upon my previous work, noting the parallels between burn injury and Spike Protein Disease/Severe COVID and Long COVID an important realization came to mind. Severity of burn injury is not only related to Degree of burn, but also Surface Area of the burn.
To begin, let us look at the Endothelium and the Skin.
Endothelial cells (ECs) form the lining of all blood and lymphatic vessels within the vascular tree. The adult human body contains at least one trillion endothelial cells, which weigh more than 100 g and cover a surface area of more than 3000 square meters.
The endothelium: A primer
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/the-endothelium-a-primer
Skin is our largest organ—adults carry some 8 pounds (3.6 kilograms) and 22 square feet (2 square meters) of it.
Skin
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/skin-1
I believe the reader will now understand the point. Remember, a Burn is an Injury. Nothing more. The Spike Protein injurs the endothelium in a parallel way to how insults burn the skin. With such a vast surface area for the Spike Protein to attack, is it any wonder that the body reacts as if it had been severely burned?
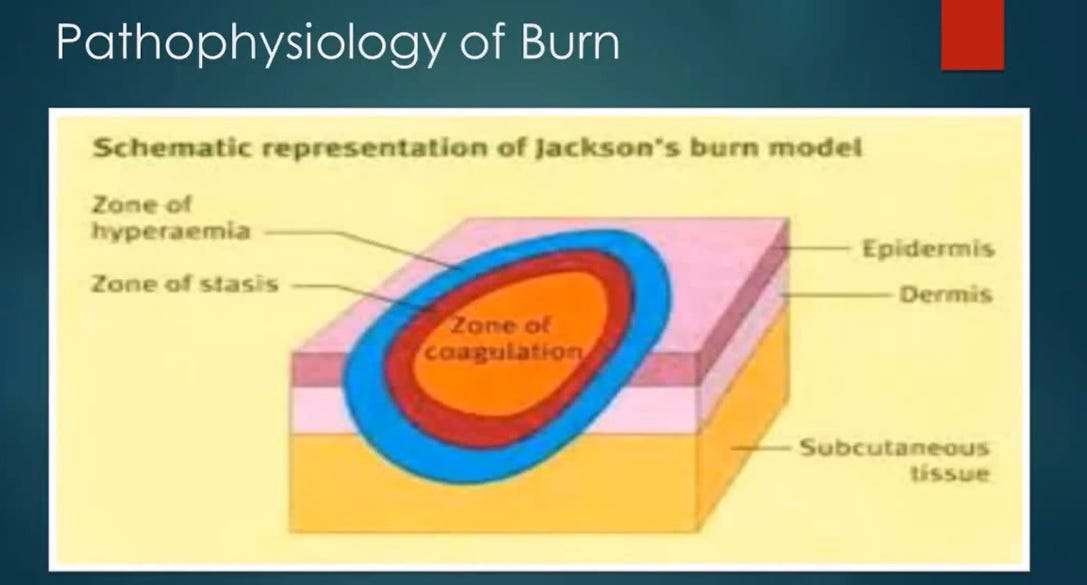
Let us look at the Jackson’s Burn Model:
In particular, let us look at the Zone of Coagulation:
Zone of coagulation—This occurs at the point of maximum damage. In this zone there is irreversible tissue loss due to coagulation of the constituent proteins.
ABC of burns
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC421790/
Now, bear with me. Remember, we are looking at Parallels – not mechanisms which are exactly the same. The Spike Protein has a parallel effect on the endothelium, as burn injury does to the skin:
SARS-CoV-2 S protein at a similar concentration (~10 μg/mL) as the viral load in critically ill patients can cause directly blood coagulation and thrombosis in zebrafish model.
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein causes blood coagulation and thrombosis by competitive binding to heparan sulfate
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8553634/
If we look at Jackson’s Burn Model closely, we can see that there can ONLY be third degree burns to the Endothelium as it is one cell layer thick. There are not five layers of epidermis and two layers of dermis to be “burned.”
The reaction of the body, if we look at the systemic effects of a major burn, are precisely those of Spike Protein Disease (injury) Severe/Acute COVID and Long COVID. Please refer to the graphics at the beginning of the post.
This is distressing, yet it also may be a window into how to successfully treat those suffering from Spike Protein/COVID related disease.
What I find fascinating is that Vitamin C. Heparin and Inhibitors of Kinin are proposed as therapeutics for major burns.
Please watch this excellent video on burns, for further understanding:






I have been following you religiously, even researching your suggested supporting studies so I can get pretty close to feeling like I have a handle on where you are going with your work. For me, you have consistently produced the most focused, pertinent and valuable information on the internet. It is fascinating to witness over the months how you've methodically (most of the time!) worked your way to this current piece. Know this. I --and most everyone else on your stack-- am forever grateful.
Interesting and very informative research as always... many thanks for sharing.
(Just a quick note that i wanted to share with you and your readers) :
Vitamin C, Heparin, and inhibitors of Kinin have been proposed as therapeutics for major burns due to their potential to reduce the severity of burn injuries...
Major burns can cause significant tissue damage, inflammation, & oxidative stress, which can lead to complications such as infection, organ failure, and even death.
Vitamin C as a potent antioxidant, can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which can be beneficial in reducing tissue damage & promoting healing in burn injuries. (Vitamin C also plays a critical role in collagen synthesis, which is important for wound healing).
Heparin, an anticoagulant medication can help prevent blood clots from forming in the damaged tissues of burn injuries. (Blood clots impedes blood flow and impedes the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the affected tissues, which can delay healing and increase the risk of infection).
Inhibitors of Kinin are medications that can help reduce inflammation and pain in burn injuries. Kinins are naturally occurring substances in the body that are released in response to tissue damage and can cause inflammation and pain.
Inhibitors of Kinin can help reduce the release of these substances, thst can help reduce inflammation & pain in burn injuries.
Overall, these medications have shown promise in reducing the severity of burn injuries and improving patient outcomes.