An Urgent Warning: Reactive Systemic Amyloidosis Induced by the Spike Protein
May Be Causing Many Sudden Deaths and Much of the Current Cachexia-Like Long COVID
I believe I have finally found the mechanism which may be causing a virulent and extremely rapid systemic amyloidosis, which may be leading to many of the sudden deaths being observed. Additionally, it may also explain much of Long COVID.
The key to understanding what I believe is happening begins with the Spike Protein and its apparent ability to induce high levels of Serum Amyloid A. Let us look at a paper on MIS-C which explains:
In this longitudinal multi-institutional study, we applied multi-omics (analysis of soluble biomarkers, proteomics, single-cell gene expression and immune repertoire analysis) to profile children with COVID-19 (n = 110) and MIS-C (n = 76), along with pediatric healthy controls (pHCs; n = 76). pCOVID-19 was characterized by robust type I interferon (IFN) responses, whereas prominent type II IFN-dependent and NF-κB-dependent signatures, matrisome activation and increased levels of circulating spike protein were detected in MIS-C, with no correlation with SARS-CoV-2 PCR status around the time of admission.
Patients with MIS-C had increased levels of several inflammatory biomarkers (serum amyloid A (SSA1), CRP, ferritin, CXCL10, sST2/sIL-33R and CXCL9) and of B natriuretic peptide (NPPB.1), the latter consistent with cardiac involvement in MIS-C. GSEA showed hyperactivation of the matrisome-associated response.
Immunopathological signatures in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and pediatric COVID-19
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-022-01724-3
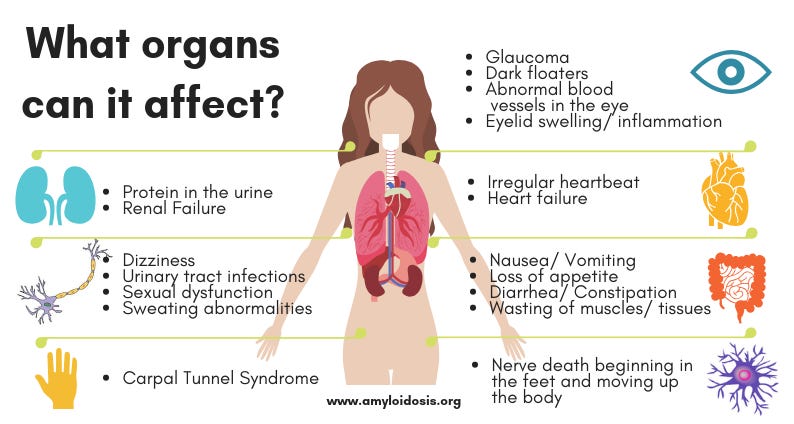
There happens to be a disorder which is caused by an elevated level of Serum Amyloid A, this is Reactive Systemic Amyloidosis.
The tissue deposits from patients with reactive amyloidosis contain amyloid protein AA, which is an amino terminal fragment of an acute phase protein called serum amyloid A protein (SAA).46-48 The acute phase proteins include coagulation proteins, complement proteins, transport proteins, protease inhibitors, and other proteins that are synthesized and released by the liver after tissue injury. The serum concentrations of many of these proteins increase twofold to threefold after injury, but the observed increase for two such proteins, C-reactive protein (CRP) and SAA, is much greater. Presumably, this group of proteins plays an important role in the inflammatory process and in tissue repair after injury. Reactive systemic amyloidosis has been observed in humans and many animal species. In humans, necropsy surveys have shown that it has a prevalence of slightly less than l%. Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common predisposing inflammatory condition, although amyloidosis will develop in less than 10% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, leprosy, and osteomyelitis previously had been the more important predisposing inflammatory diseases.
The Pathogenesis of Reactive Systemic Amyloidosis
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/j.1939-1676.1989.tb00326.x
The increase in Serum Amyloid A, I believe, is inducing an extremely rapid form of amyloidosis: Reactive Systemic Amyloidosis.
Serum amyloid-A protein (SAA) is the putative precursor of amyloid-A (AA) protein which forms the fibrils in reactive systemic or secondary amyloidosis. By means of a novel immunoradiometric assay, the concentration of SAA was found to be greatly elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile chronic arthritis and correlated with activity of their primary disease. However, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus SAA levels were only modestly raised, even in those with severe active disease, unless significant intercurrent microbial infection was also present. In Crohn's disease SAA levels showed a pattern similar to that seen in rheumatoid arthritis, whereas in ulcerative colitis it resembled that of systemic lupus erythematosus. The level of SAA response in these different disorders corresponds with the incidence of reactive systemic amyloidosis in them. These observations support the view that major increases in SAA levels are a necessary condition for the deposition of this form of amyloid and suggest that prospective monitoring of the SAA concentration in predisposing diseases may help to identify those individuals who are most at risk for amyloidosis.
SERUM AMYLOID-A PROTEIN CONCENTRATION IN INFLAMMATORY DISEASES AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO THE INCIDENCE OF REACTIVE SYSTEMIC AMYLOIDOSIS
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S014067368290321X
I will continue to expound on this hypothesis. I wanted to publish the foundation of this hypothesis immediately for feedback and to provide a warning to all of us as to the potential implications of exposure to the Spike Protein.

There are no words to express my anger at all this human damage.
Why does the V word fail to appear in your article? It's the elephant is the room.