Friday Hope: Magnolia officinalis (Magnolia Bark): Inhibiting NOX and SARS-CoV-2 Replication
This potent nutraceutical also provides Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer benefits.
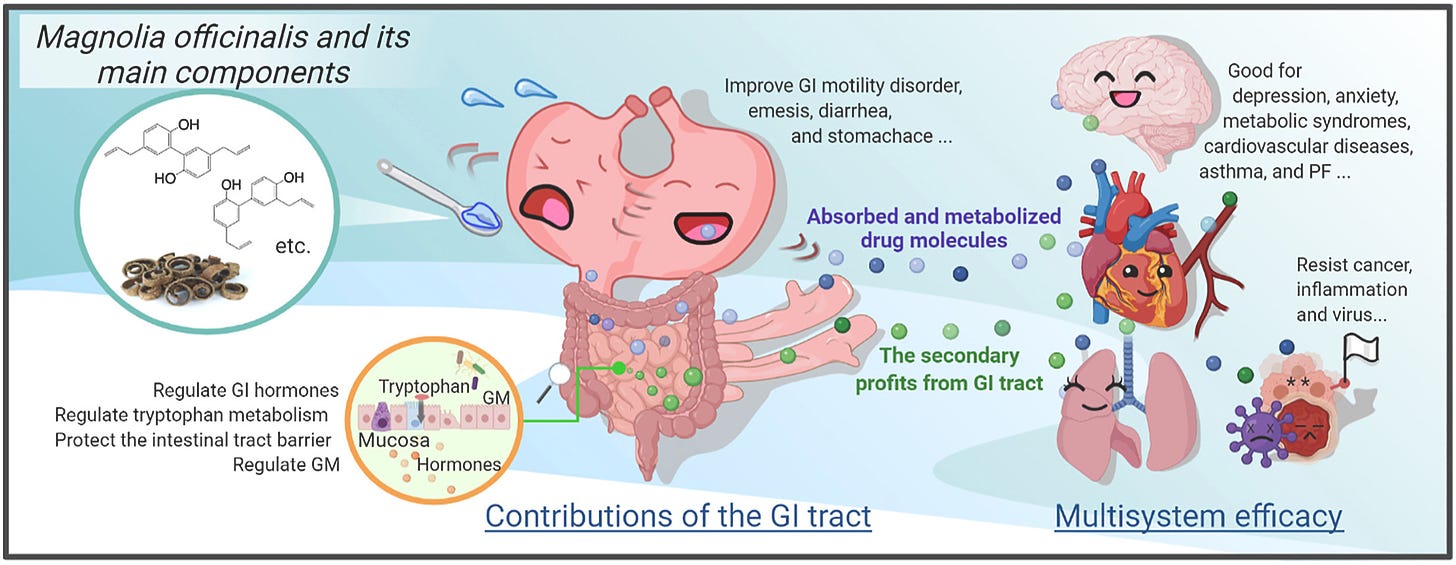
Magnolia officinalis Cortex has plenty of pharmacological activities and gastrointestinal (GI) tract contributes a lot to it. In addition to rich gastrointestinal activity, Magnolia officinalis can also exert multisystem efficacy through GI absorption and transport or secondary effects based on intestinal effects.
The rich pharmacological activities of Magnolia officinalis and secondary effects based on significant intestinal contributions
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874121007534
Given my recent findings that the Spike Protein and SARS-CoV-2 activates NOX5, which can lead to the induction of small vessel disease (please see my previous post), I sought a natural therapeutic to ameliorate this activity. Nature does, indeed, provide a nutraceutical with the ability to inhibit NOX – and a whole lot more. Let me introduce you to Magnolia officinalis (Magnolia Bark).
One type — Magnolia officinalis — is commonly called the houpo magnolia, or sometimes simply “magnolia bark.”
Typically, magnolia bark is bark of the houpo magnolia tree that has been stripped away from it branches and stems to make supplements.
The leaves and flowers from the tree are sometimes used as well.
The bark is particularly rich in two neolignans that are believed to be responsible for its medicinal properties — magnolol and honokiol.
Neolignans are a type of polyphenol micronutrient in plants. Polyphenols are highly valued for their antioxidant levels and believed to offer many health benefits.
Some of the conditions that magnolia bark has traditionally been used to treat include asthma, anxiety, depression, stomach disorders, and inflammation.
Magnolia Bark: Benefits, Usage, and Side Effects
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/magnolia-bark
Let’s talk first about that lignan Honokiol. Right away Magnolia Bark shows its promise in treating SARS-CoV-2 as Honokiol is able to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication. So, clearly, it demonstrates an ability to treat acute COVID.
In this study, we determined that honokiol protected Vero E6 cells from SARS-CoV-2-mediated cytopathic effect, with a 50% effective concentration of 7.8 μM. In viral load reduction assays, honokiol decreased viral RNA copies as well as viral infectious progeny titers. The compound also inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in the more relevant human A549 cells expressing angiotensin converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2. Time-of-addition and other assays showed that honokiol inhibited virus replication at a post-entry step of the replication cycle. Honokiol was also effective against more recent variants of SARS-CoV-2, including Omicron, and it inhibited other human coronaviruses as well.
Honokiol Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Cell Culture at a Post-Entry Step
https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/spectrum.03273-22
In addition to the above acute COVID benefit, Magnolia Bark may be able to treat those with Long COVID and/or Spike Protein exposure pathologies. In particular, Magnolia Bark can inhibit NOX, which the Spike Protein/SARS-CoV-2 activates. Activation of NOX (NOX5 especially) is associated with the induction of small vessel disease which can lead to fibrosis and organ destruction.
The bark of magnolia has been used in oriental medicine to treat a variety of remedies, including some neurological disorders [81]. Magnolol (Mag) and honokiol (Hon) are isomers of polyphenolic compounds from the bark of Magnolia officinalis, and have been identified as major active components exhibiting antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. It has been reported that exposure of Hon and Mag to neurons for 24 h did not alter neuronal viability, but both compounds inhibited superoxide production, a pathway known to involve NADPH oxidase. This study highlighted the important role of NADPH oxidase in mediating oxidative stress in neurons and microglial cells and has unveiled the role of IFNγ in stimulating the MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway for activation of NADPH oxidase in microglial cells. Hon and Mag offer anti-oxidative or anti-inflammatory effects, at least in part, through suppressing IFNγ-induced p-ERK1/2 and its downstream pathway.
Natural Compounds as Modulators of NADPH Oxidases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3863456/
Furthermore, there is much that Magnolia Bark offers in treating other aspects of Long COVID/Spike Protein exposure and supporting health in general. For instance, there is evidence that Magnolia Bark mediates inflammatory indicators upregulated by SARS-CoV-2/Spike Protein.
As discussed in the previous section, the NO production, the expressions of iNOS, IL-1β, TNF-α and COX, and the generation of eicosanoids, in addition to the activation levels of MAPKs, AP-1, and NF-κB pathways, may reflect the degree of inflammation and have become important indicators with which to assess inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes (Lee et al., 2011). An impressive series of studies has shown that all of these major indicators are positively impacted by Magnolia lignans, even if the full anti-inflammatory mechanisms have not yet been elucidated (Choi et al., 2007; Lin et al., 2007; Munroe et al., 2007; Kang et al., 2008; Lee et al., 2011). Upregulating signaling cascades composed of Ras, Raf, and MAPK, downregulating the activation of NF-κB, and blocking NF-κB activation mediated by CD40 and latent membrane protein 1 are speculated to be the action mechanism of Magnolia lignans (Lin et al., 2007; Kim and Cho, 2008; Lee et al., 2011).
Additionally, there is evidence for treating cancer as Magnolia Bark is cytotoxic to cancer cells.
Several constituents of M. officinalis, mainly lignans, have been widely reported to be cytotoxic, which is a possible clue to new anti-cancer compounds (Lee et al., 2011). At low concentrations (up to 3 µmol/L), they can induce apoptosis in human cancer cell lines, whereas they do not inhibit the growth of human untransformed cells (Kong et al., 2005). Honokiol was reported to possess higher activity than magnolol in the induction of apoptosis (Kong et al., 2005). Obovatol increased the susceptibility to chemotherapeutic agents at low concentrations, around 5 µmol/L (Lee S.Y. et al., 2009).
Biological activity and toxicity of the Chinese herb Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E. Wilson (Houpo) and its constituents
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5365644/
I have stated this before: Nature never ceases to amaze me. The abundance of life-sustaining, life-nurturing and healing nutraceuticals is overwhelming. A great tragedy of “Modern” medicine is that many doctors (pharma reps), and certainly the MSM, do not report new findings or teach known natural compound benefits to patients or public. We will search. We will learn.
Please have a splendid early summer weekend! It is lovely here in Northern Vermont. Seventy-one degrees, gentle breeze, crystal clear skies. And, yes! The Magnolias are still blooming in many places!

Our ancestors survived long enough to reproduce and pass Faith in God, Culture and any tech they had to us as next generations. People have always had the same predisposition towards illness and injury since The Garden of Eden.
Only logical for Nature to have been their Pharmacy; a Pharmacy the eugenicist Rockefeller's sought to remove as options to Medical Care leaving only their POISONS as weapons and for economic advantage...All about CONTROL.
Gods treasure